How do I create a S/MIME certificate for my email address
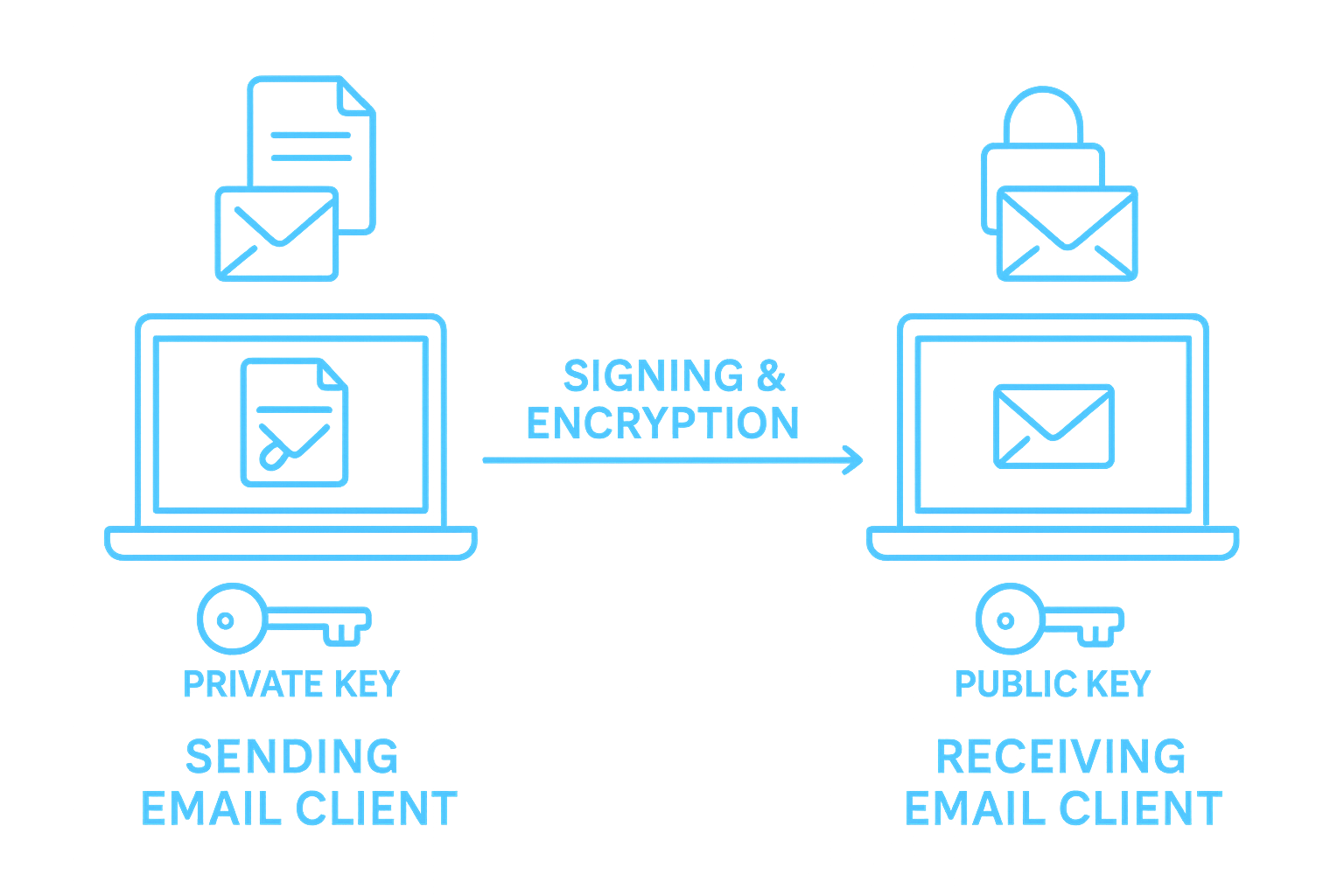
An S/MIME certificate is a digital certificate (X.509-based) that enables you to:
Email encryption and decryption
Protecting message confidentiality by ensuring only the intended recipient can read the content.
Email and documenent signing
This ensuring message or documents integrity (no tampering) and authenticity (verifying identity).
Unlike TLS (which only protects email while in transit), S/MIME ensures end-to-end security between you and your recipient. Certificates can be self-signed, but using a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) makes validation easier and improves trustworthiness
The Key Pair we will create can then be used to sign, verify, encrypt, and decrypt email.
View Script
An S/MIME certificate is a digital certificate (X.509-based) that enables you to:
Email encryption and decryption
Protecting message confidentiality by ensuring only the intended recipient can read the content.
Email and documenent signing
This ensuring message or documents integrity (no tampering) and authenticity (verifying identity).
Unlike TLS (which only protects email while in transit), S/MIME ensures end-to-end security between you and your recipient. Certificates can be self-signed, but using a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) makes validation easier and improves trustworthiness
The Key Pair we will create can then be used to sign, verify, encrypt, and decrypt email.

View Script